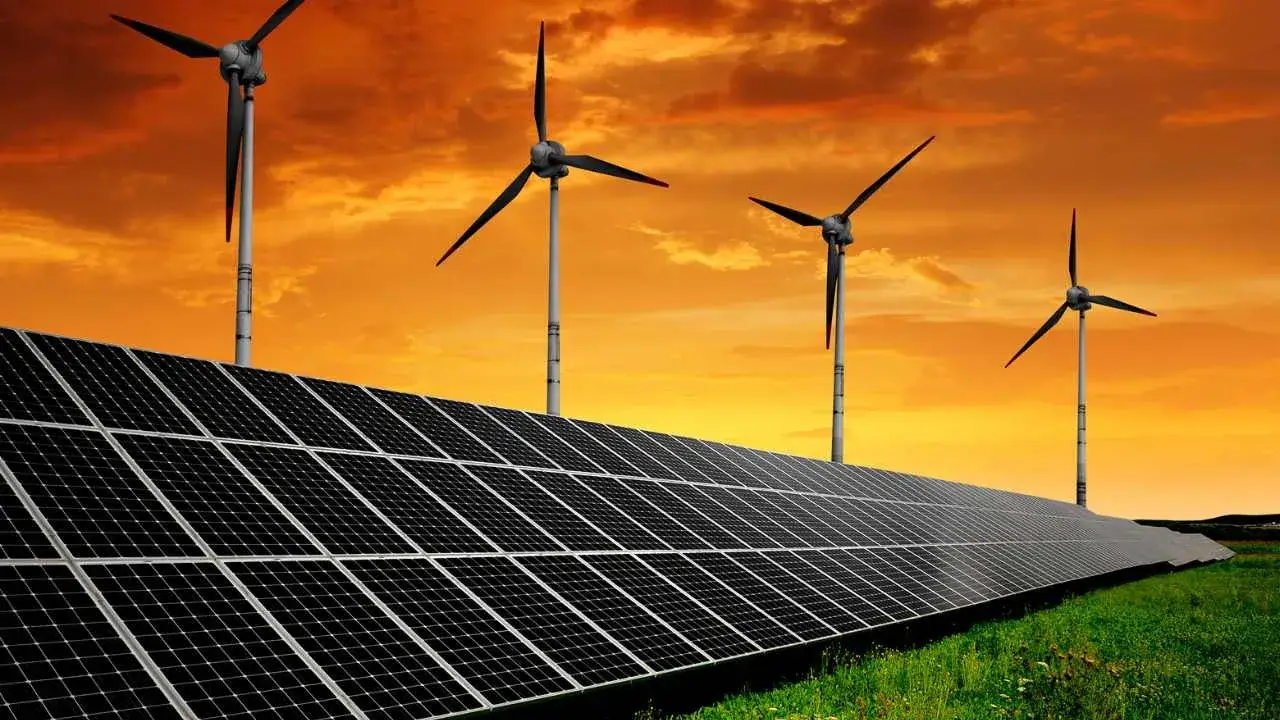
As the effects of climate change grow increasingly severe, the global shift toward renewable energy has become more urgent than ever. Unlike fossil fuels, which emit greenhouse gases and deplete finite natural resources, renewable energy sources offer sustainable, cleaner alternatives for powering the world. From the sun above us to the wind sweeping across plains, nature provides powerful tools that can meet our energy needs without harming the planet.
What Are Renewable Energy Sources?
Renewable energy comes from sources that naturally replenish over time. Unlike coal, oil, or natural gas, which take millions of years to form, renewable energy sources are constantly available in our environment. The most common forms include:
-
Solar Energy: harnessed from sunlight using photovoltaic (PV) panels or solar thermal systems.
-
Wind Energy: generated using wind turbines that convert air movement into electricity.
-
Hydropower: produced by moving water through dams or flowing rivers.
-
Geothermal Energy: drawn from the Earth’s internal heat to power turbines or provide heating.
-
Biomass Energy: created by burning organic materials such as wood, crop waste, or biofuels.
These sources differ in how they operate, but they all share one core principle: minimal environmental impact with long-term sustainability.
The Benefits of Renewable Energy
-
Environmental Protection
Renewables produce little to no greenhouse gas emissions, helping reduce global warming and air pollution. -
Energy Independence
Countries can reduce reliance on imported fossil fuels and develop domestic renewable infrastructure, enhancing energy security. -
Economic Growth
The renewable energy sector has become a significant job creator worldwide, offering new careers in installation, maintenance, and innovation. -
Sustainable Development
Clean energy helps improve health outcomes, reduce energy poverty in developing regions, and support long-term ecological balance.
Challenges in Transitioning to Renewables
While renewable energy is promising, it’s not without obstacles:
-
Storage Limitations: Solar and wind energy are intermittent; they require efficient storage systems like batteries to supply power consistently.
-
High Upfront Costs: Although operational costs are low, initial investment in renewable infrastructure can be expensive.
-
Grid Integration: Older electricity grids in many countries were built for fossil fuels and require upgrades to handle renewable energy sources.
Despite these challenges, technological advancements are rapidly making renewables more reliable and cost-effective.
Global Trends and Future Outlook
According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), renewable sources are expected to supply nearly 50% of global electricity by 2030. Countries like Denmark, Iceland, and Costa Rica already generate most of their energy from renewables, serving as examples of what’s possible.
Innovation is also accelerating:
-
Floating solar farms
-
Offshore wind turbines
-
Next-gen battery storage
-
Hydrogen fuel technologies
All point toward a cleaner, smarter energy landscape ahead.
Conclusion
Renewable energy isn’t just a trend it’s the future. By investing in solar, wind, hydropower, and other clean technologies, humanity can reduce its carbon footprint, create economic opportunity, and ensure a livable planet for future generations. The energy revolution is here and it’s powered by the forces of nature.